Steam Boiler Damage: 3 Key Factors and Solutions
Hardness:
Hardness: Excessive minerals dissolved in water can increase water hardness, leading to scale deposits on the boiler’s surfaces. Even a scale layer as thin as 1/8 inch can reduce boiler efficiency by up to 25%. These scales act as insulators, hindering heat transfer and increasing fuel consumption. Additionally, scale deposits can cause local overheating and potential failure of boiler metals. Fortunately, this issue can be easily addressed with a water softener, and those in areas with naturally soft water are even luckier.
Corrosion:
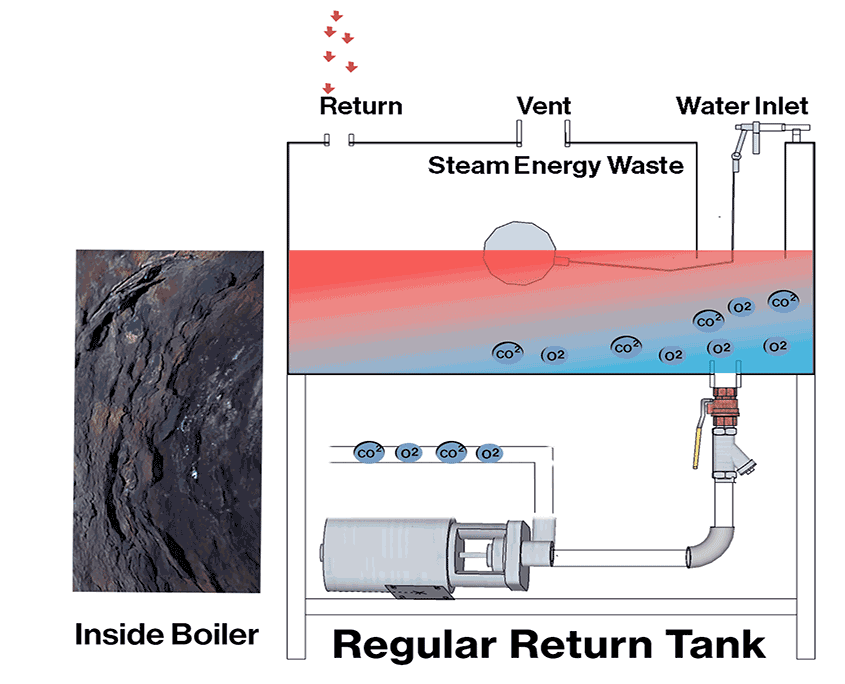
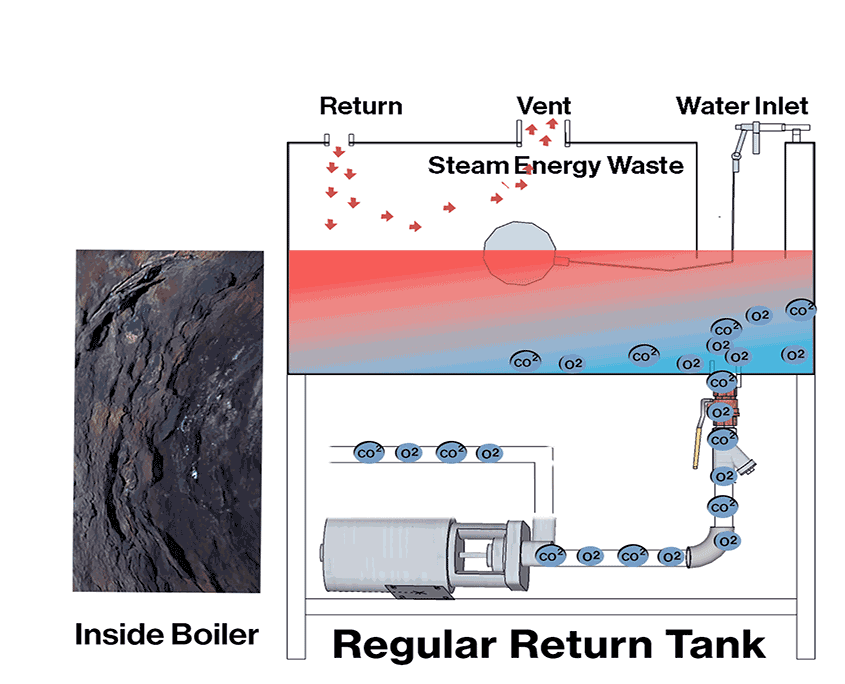
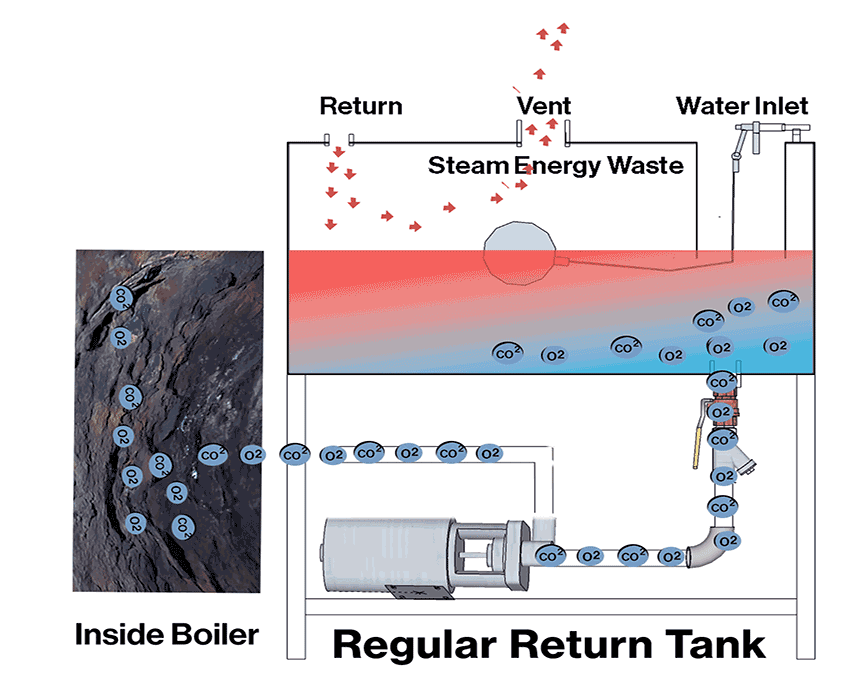
Dissolved Oxygen (O2) and Carbon Dioxide (CO2) pose a greater risk as they silently corrode the boiler from the inside out. Oxygen is the main culprit, corroding the boiler metal up to ten times faster than CO2. When both gases are present, the corrosion rate can accelerate by 40 times, significantly shortening the boiler’s lifespan.

O2 & CO2 Removal Methods:
Deaerators: While capable of completely removing dissolved oxygen & Carbon Dioxide, they are expensive and large.
Preheated return tanks: Utilize boiler steam to preheat the return tank, reducing O2 & CO2 solubility.
Oxygen scavenger chemicals: Help reduce oxygen only but are not perfect. Moisture can be transported by steam.
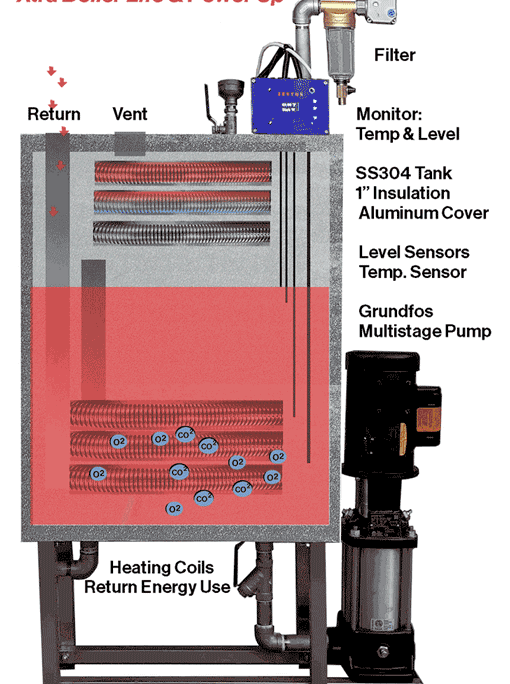
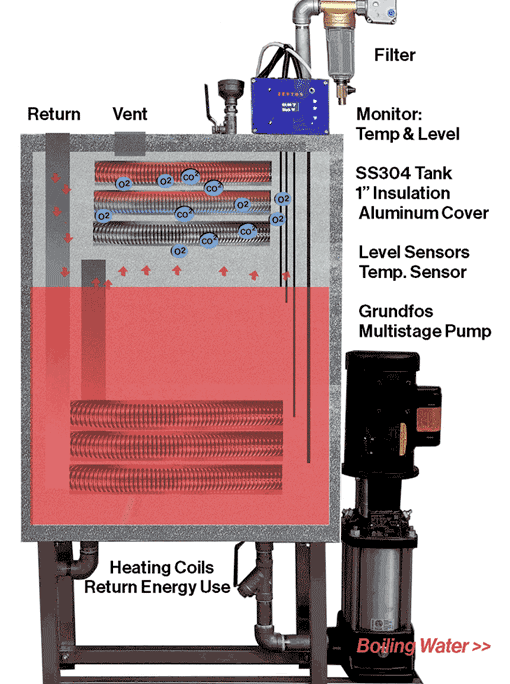
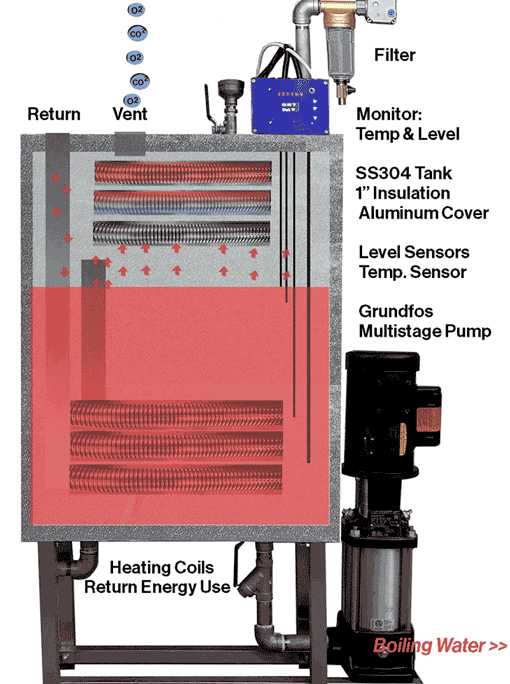
ZESTOS Solution:
ZESTOS is a patented boiler return system that dramatically extending boiler life.
Eliminates dissolved oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Stronger feed water is supplied by boiling.
The system withstands Grundfos multi-stage pumps and up to 248°F.
Our microchips finely control water to prevent wasting water.
Saving money and the planet with ZESTOS. Protect your boiler and the environment by reusing as much wasted steam heat as possible.
Conclusion:
By understanding the key causes of steam boiler damage and implementing effective preventive measures like water softening, oxygen removal, and ZESTOS technology, you can ensure optimal boiler performance, longevity, and environmental sustainability.